Soft tissue injuries (STIs) are among the most common, and often overlooked types of injuries following a car accident. These injuries affect the muscles, ligaments, and tendons and can range from minor strains to debilitating conditions like whiplash. While they may not always be visible on X-rays, soft tissue injuries can lead to chronic pain and long-term complications if left untreated.
In this article, we’ll break down what soft tissue injuries are, how they happen, common symptoms, treatment options, and why early diagnosis is important after an auto accident.
What Is a Soft Tissue Injury?
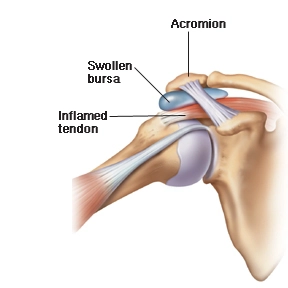
A soft tissue injury involves damage to the muscles, tendons, or ligaments of the body. These are the structures that support joints and enable movement. Common soft tissue injuries include:
- Sprains – Overstretching or tearing of ligaments.
- Strains – Tearing or stretching of muscles or tendons.
- Tendonitis – Inflammation of the tendons.
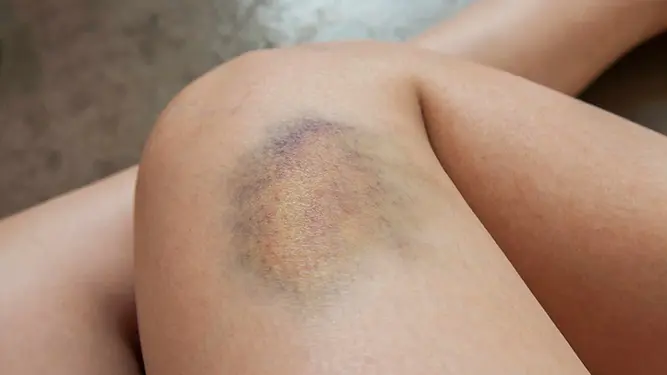
- Contusions (bruises) – Direct trauma that damages muscle fibers and small blood vessels.
- Bursitis – Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints.
- Whiplash – A neck injury caused by rapid back-and-forth movement of the head.
Soft tissue injuries can occur from various situations such as sports, falls, and repetitive use. However, car accidents are one of the leading causes due to the intense forces involved in collisions, even low-speed impacts.
How Car Accidents Cause Soft Tissue Injuries
During a collision, your body absorbs a sudden jolt or impact. Even with seat belts and airbags, your limbs, neck, and torso can twist or collide with hard surfaces inside the vehicle. These movements or impacts stretch tissues beyond their normal range, causing damage.
Soft tissue injuries in car accidents may result from:
- Whipping motion of the neck (e.g., whiplash from rear-end collisions)
- Bracing for impact with arms or legs
- Being struck by airbags or seatbelts
- Blunt trauma from contact with the steering wheel, door, or dashboard
Symptoms of Soft Tissue Injuries
Symptoms may appear immediately or take hours, or even days to become noticeable. Be on the lookout for:
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling or inflammation
- Bruising or discoloration
- Limited range of motion
- Stiffness or aching muscles
- Weakness in the injured area
- Headaches or fatigue (especially in whiplash)
If you experience any of these symptoms after an accident, it’s essential to get medical attention. Ignoring symptoms may delay healing or increase the risk of long-term damage.
Common Types of Soft Tissue Injuries from Car Accidents
✅ Sprains and Strains
A sprain occurs when ligaments are stretched or torn. A strain affects muscles or tendons. These injuries often happen in the neck, back, shoulders, and legs after a crash. They can cause sharp pain, muscle spasms, and joint instability.
✅ Tendonitis
This is inflammation of a tendon due to overuse or trauma. After an accident, tendonitis may develop from repetitive movements during impact or from trying to brace yourself. It may take days for the inflammation to surface.
✅ Contusions (Bruising)
Contusions occur from blunt force trauma. In car accidents, this might happen when your body strikes parts of the vehicle or is restrained by a seatbelt. While bruises can appear minor, they can also indicate deeper muscle or tissue damage.
✅ Bursitis
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that cushions joints. Trauma from a collision can inflame these sacs, especially around the shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows, causing painful swelling known as bursitis.
✅ Whiplash
Whiplash is the most talked-about soft tissue injury following car accidents, especially rear-end collisions. It affects the neck and upper spine and can cause stiffness, headaches, and nerve symptoms. Unfortunately, whiplash may not show up on X-rays, so an MRI or other imaging may be required to properly diagnose it.
Diagnosing and Documenting Soft Tissue Injuries
Unlike broken bones, soft tissue injuries are harder to detect using standard diagnostic tools. X-rays won’t show ligament or muscle damage. In many cases, providers rely on:
- Physical exams
- MRI or ultrasound imaging
- Chiropractic evaluations
- Orthopedic assessments
If you’ve been in a car accident, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Not only does this support your recovery, it also strengthens your personal injury case. Insurance companies often question the legitimacy of soft tissue claims due to their “invisible” nature.
Treatment Options for Soft Tissue Injuries
💡 Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors specialize in treating musculoskeletal trauma. Chiropractic adjustments and therapeutic exercises help reduce inflammation, restore alignment, and encourage natural healing. Many accident doctors use chiropractic care as a primary method for managing STIs.
💡 Physical Therapy
PT can help restore flexibility, strength, and range of motion. It’s especially effective for neck and back injuries following a crash.
💡 Imaging (MRI/CT scans)
Your provider may order an MRI to detect the extent of soft tissue damage. This is common in personal injury claims and can be crucial for legal and medical documentation.
💡 At-Home Care (The R.I.C.E. Method)
For mild injuries, initial care at home includes:
- Rest – Stop using the injured area and avoid further strain.
- Ice – Apply ice for 15–20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling.
- Compression – Use a compression bandage to support and reduce inflammation.
- Elevation – Elevate the injured area above heart level to decrease swelling.
Delayed or Incomplete Healing: A Warning Sign
Some soft tissue injuries are never fully healed especially if left untreated or managed improperly. Untreated damage can lead to:
- Chronic pain
- Scar tissue formation
- Decreased mobility
- Recurrent injury
Don’t assume that your pain or stiffness will simply “go away.” Early and consistent treatment is critical to prevent long-term effects. Insurance companies often deny claims when there are gaps in care, so don’t skip appointments, even if you’re feeling better temporarily.
Why Emergency Rooms Are Not Enough
After a car crash, going to the ER is a smart first step, especially to rule out life-threatening injuries like fractures or internal bleeding. But ERs often do not treat soft tissue injuries in depth. Most patients are sent home with painkillers and a recommendation to “follow up if needed.”
That’s why you should always schedule an appointment with a car accident doctor or personal injury chiropractor shortly after your ER visit.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Ignore Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries are real, painful, and can have long-term consequences. They deserve proper attention, diagnosis, and care. Whether you’re dealing with neck pain from whiplash or a bruised shoulder from the seatbelt, getting treated early increases your chances of full recovery, and helps protect your legal rights.
🚨 Have You Been Injured in a Car Accident?
Don’t wait. Contact a doctor who specializes in personal injury care today. The longer you delay, the more difficult it becomes to heal, and to prove your case.


 Since 2012,
Since 2012, 

